Ensuring PCI Compliance in the Tech Industry

Importance of PCI Compliance for Tech Companies
PCI compliance is essential for tech companies to maintain the security and integrity of payment card transactions. Achieving PCI compliance helps prevent data breaches. Data breaches can cause severe financial losses and harm a company's reputation. Tech companies must prioritize PCI compliance to meet regulatory standards and demonstrate their commitment to data security.
Protecting Cardholder Data in Tech Industry
Protecting cardholder data is a fundamental aspect of PCI compliance. Key practices include:
- Encryption: Encrypt cardholder data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Limit access to cardholder data to only authorized personnel.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address weaknesses.
Meeting PCI DSS Requirements in Technology Firms
Meeting PCI DSS requirements is essential for tech companies to comply with regulations and secure cardholder data. Key requirements include:
- Build and Maintain a Secure Network: Install and maintain firewalls to protect cardholder data and ensure a secure network. Implementing strong passwords and access control measures is crucial.
- Protect Cardholder Data: Meeting PCI DSS requirements is essential for tech companies to comply with regulations and secure cardholder data. Use and regularly update antivirus software.
- Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program: Develop and maintain secure systems as part of a vulnerability management program. Implement strong access control measures.
- Regularly Monitor and Test Networks: Monitor and test networks regularly to track access to network resources and cardholder data.
Understanding Data Breach Impacts on Technology Firms

Common Causes of Data Breaches in Tech Sector
Various factors often cause data breaches in the tech sector. One primary cause is cyber attacks. These attacks can range from phishing scams, tricking employees into providing sensitive information, to sophisticated malware designed to infiltrate systems. Another significant cause is weak security protocols.
Cyber Attacks Leading to Data Breaches
Cyber attacks are a leading cause of data breaches in the tech industry. These attacks can take many forms, including:
- Phishing: Attackers send fraudulent emails to trick recipients into revealing personal information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software encrypts data, with attackers demanding payment for the decryption key.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service): Attackers overwhelm a system with traffic, causing it to crash and potentially exposing weaknesses.
Internal Vulnerabilities in Tech Companies
Internal vulnerabilities within tech companies can significantly contribute to data breaches. These vulnerabilities often arise from inadequate security practices, such as poor password management and lack of encryption. Insider threats are another critical concern, where employees with access to sensitive information misuse it either maliciously or accidentally. Additionally, outdated software and systems can present exploitable weaknesses.
Implementing Data Loss Prevention Strategies in Tech Companies

Best Practices for Data Loss Prevention
Implementing best practices for data loss prevention helps tech companies mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Key practices include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and weakness assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses.
- Data Classification: Categorize data based on its sensitivity and apply appropriate protection measures accordingly.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly address and mitigate data breaches.
Employee Training for Data Security Awareness
Employee training is a critical component of an effective data loss prevention strategy. Well-informed employees are the first line of defense against data breaches and other security threats. Key training initiatives include:
- Security Awareness Programs: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about data security best practices and emerging threats.
- Phishing Simulations: Run phishing simulations to help employees recognize and respond properly to phishing attempts.
- Data Handling Procedures: Train employees on proper data handling procedures, including the use of secure file-sharing methods.
- Policy Compliance: Ensure employees understand and comply with company data security policies and procedures.
Utilizing Advanced Data Loss Prevention Tools
Advanced data loss prevention tools are essential for monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Key features of these tools include:
- Data Monitoring: Continuously monitor data activities to detect suspicious behavior and potential threats.
- Automated Alerts: Configure automated alerts to notify security teams of any unusual activities or potential data breaches.
- Endpoint Protection: Implement endpoint protection solutions to secure devices and prevent data loss from endpoints.
- Data Leak Detection: Use tools that can detect and block data leaks, both within the organization and through external channels.
- Compliance Management: Ensure that DLP tools support compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA.

Effective Data Encryption Techniques for Protection
Data encryption is a critical method for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. Effective encryption techniques include:
- Symmetric Encryption: Use symmetric encryption, which utilizes a single key for both encryption and decryption. It is efficient for encrypting large amounts of data quickly.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Use asymmetric encryption, which employs a pair of keys (public and private) for encryption and decryption. This method provides a higher level of security, especially for transmitting data.
- End-to-End Encryption: The sender encrypts the data on their device, and only the recipient can decrypt it. This prevents middlemen from accessing the data.
Implementing Secure Backup Solutions
Secure backup solutions are essential for ensuring data availability and integrity. They protect against breaches, hardware failures, or other disruptions. Key components of a secure backup strategy include:
- Regular Backups: Regularly schedule backups to protect the most recent data.
- Offsite Storage: Store backups in a secure offsite location to protect against physical damage or localized disasters.
- Encryption: Encrypt backup data to prevent unauthorized access during storage and transmission.
- Automated Backup Systems: Use automated systems to reduce the risk of human error and ensure consistent backup processes.
Regular Audits and Monitoring for Data Protection
Regular audits and monitoring are crucial for maintaining a robust data protection framework. Key steps include:
- Security Audits: Conduct thorough security audits to evaluate the effectiveness of security measures and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring systems to track data access and usage in real time.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and regularly update incident response plans to address data breaches and other security incidents swiftly.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure data protection practices comply with regulations and industry standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Managing Security Breaches in the Technology Industry

Steps to Take After a Security Breach
Taking the right steps immediately after a security breach is crucial to mitigating damage and protecting sensitive data. Key steps include:
- Identify the Breach: Quickly determine the scope and nature of the breach. Identify affected systems and data.
- Contain the Breach: Isolate affected systems to prevent further unauthorized access or damage.
- Assess the Damage: Evaluate the extent of data loss and its potential impact on the organization.
- Notify Stakeholders: Inform stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, about the breach and its implications.
- Report to Authorities: If required, report the breach to relevant regulatory authorities and comply with legal obligations.
Immediate Response Strategies for Breaches
Effective immediate response strategies are essential for minimizing the impact of a security breach. Key strategies include:
- Activate the Incident Response Plan: Implement the pre-defined incident response plan to ensure a coordinated and efficient response.
- Communicate Clearly: Maintain transparent communication with all stakeholders, providing timely updates on the breach and response efforts.
- Preserve Evidence: Secure and preserve evidence related to the breach for forensic analysis and potential legal action.
- Conduct Root Cause Analysis: Identify the root cause of the breach to address weaknesses and prevent recurrence.
- Restore Systems: Start restoring affected systems and data while strengthening security measures during the recovery process.
Long-term Measures to Prevent Future Breaches
Implementing long-term measures is critical to preventing future security breaches and enhancing overall data security. Key measures include:
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits to identify and address weaknesses.
- Employee Training: Provide ongoing training for employees on security best practices and emerging threats.
- Update Security Policies: Regularly review and update security policies to align with current threats and industry standards.
- Invest in Advanced Security Technologies: Deploy advanced security technologies such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption.
- Develop a Culture of Security: Foster a culture that prioritizes data security at all levels of the organization.
Utilizing Database Activity Monitoring for Enhanced Security
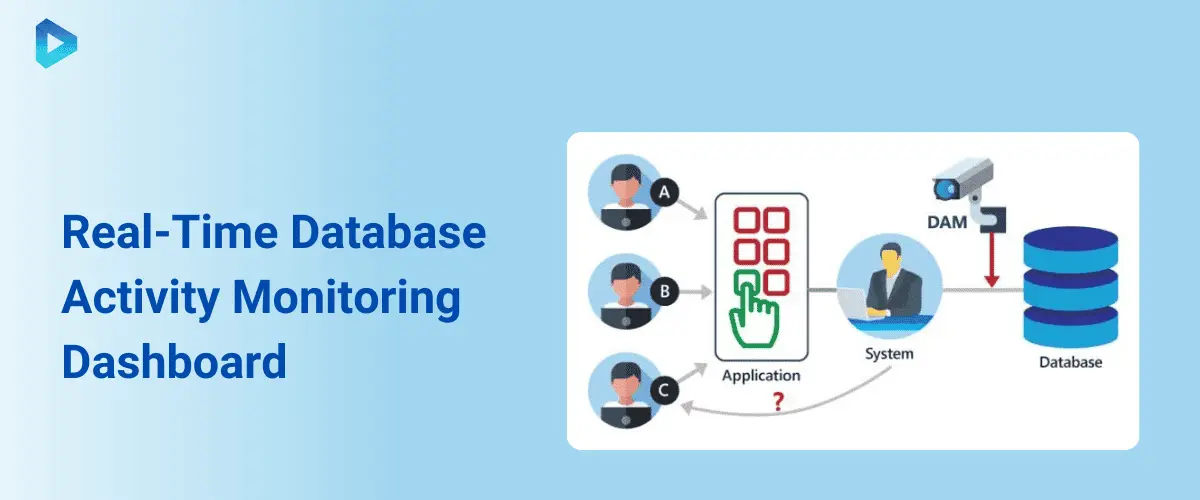
Importance of Monitoring Database Activities
Monitoring database activities is crucial for detecting and preventing unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Key benefits include:
- Real-Time Detection: Real-time detection systems help identify unusual or unauthorized activities as they occur, enabling immediate action.
- Compliance Assurance: Helps meet regulatory requirements by providing detailed audit trails and reports.
- Data Integrity: Ensures that all database activities are legitimate and aligned with security policies.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of data breaches by proactively identifying and addressing weaknesses.
Effective database activity monitoring relies on advanced tools that provide comprehensive visibility and control over database activities. Key tools include:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitors for suspicious activities and potential threats.
- Database Firewalls: Blocks unauthorized access and provides real-time monitoring and alerts.
- User Activity Monitoring (UAM): Tracks and records user actions within the database to ensure compliance and detect anomalies.
- Automated Auditing Tools: Generate detailed audit logs and reports for regulatory compliance and forensic analysis.
Analyzing and Responding to Suspicious Activity
Analyzing and responding to suspicious database activity is critical for preventing data breaches and maintaining data security. Key steps include:
- Alert Analysis: Evaluate alerts generated by monitoring tools to determine the severity and potential impact of the activity.
- Incident Response: Activate the incident response plan to address and mitigate the identified threat.
- Forensic Investigation: Conduct a thorough investigation to understand the nature and source of the suspicious activity.
- Fixing: Implement measures to address weaknesses and prevent future incidents.
- Reporting: Document the incident and response actions taken, and report to relevant stakeholders and regulatory authorities as necessary.







